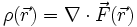The gradient is a vectorial field and found scalars vectorials.
The Rotacional is a vecorial shield and we can found vectorial shields in 3D(tridimensionales); and the diveregencia is a shield scalar and we can found vectorials field in general.
When we want measure the circulation of a shield vectorial like a function of the coordenadas, it use a vectorial function called Rotacional, que mide the circulation for unity of área when the área tiende a zero(0) on each point of the space en donde se encuntra definido el campo.
When the rotacional is nulo on the points of a region, se dice que the shield is irrotacional or conservative en dicha región.
Profe hay unas palabritas en español..es q se me olvidaron..en inglés y tengo q aprovechar antes de q me vuelva a quedar sin pc.....
Gracias
The Rotacional is a vecorial shield and we can found vectorial shields in 3D(tridimensionales); and the diveregencia is a shield scalar and we can found vectorials field in general.
When we want measure the circulation of a shield vectorial like a function of the coordenadas, it use a vectorial function called Rotacional, que mide the circulation for unity of área when the área tiende a zero(0) on each point of the space en donde se encuntra definido el campo.
When the rotacional is nulo on the points of a region, se dice que the shield is irrotacional or conservative en dicha región.
Profe hay unas palabritas en español..es q se me olvidaron..en inglés y tengo q aprovechar antes de q me vuelva a quedar sin pc.....
Gracias

 Índice
Índice